How Many Companies Use a PEO?
Robbin Schuchmann
Co-founder, Employ Borderless
A PEO (Professional Employer Organization) is a third-party company that manages HR functions of companies, like payroll management, benefits administration, compliance, and risk management. A PEO works by forming a co-employment agreement with the businesses and sharing employer responsibilities for tax and compliance purposes to reduce legal risks and costly penalties.
The overall number of U.S. companies is 208,000 that use a PEO, which shows 17% of all employers with 10 to 19 employees. The PEO industry has grown quickly since 2012, as it generates $358 billion in revenue. Businesses in professional, technical, manufacturing, and construction sectors rely on PEOs for payroll, benefits administration, and compliance support.
What is the total number of companies using PEOs?
The total number of companies using PEOs is approximately 208,000 in the U.S., most of which are small and medium-sized businesses. These 208,000 clients represent 17% of all employers with 10 to 99 employees. For example, about 39% of companies in Florida use PEOs, 20% in Georgia, 16% in New York, and only 3% in other states, which include Maryland.
There are over 500 PEOs in the United States that collectively employ about 4.5 million workers across their client companies. This number is similar to the combined total number of employees working at major U.S. companies like Walmart, Amazon, Kroger, and Home Depot. The global PEO market was valued at USD 66.23 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to USD 73.58 billion in 2025 and reach USD 170.8 billion by 2033. This value shows a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 11.10% over the expected period.
What size companies use PEOs?
The size of companies that use PEOs includes startups, small businesses, medium-sized businesses, and large enterprises. Most PEO clients are small and medium-sized businesses, with 37% having 20 to 49 employees and 28% having 10 to 19 employees. Startups with 1 to 5 employees make up 5% of PEO clients, while larger businesses with 100 to 499 employees account for just 6%, which shows that PEOs are used more often by smaller companies.
How has the PEO industry grown over time?
The PEO industry has grown from a basic employee leasing arrangement since the early 1960s into a fast-growing sector that offers payroll processing, benefits administration, and compliance support. The PEO industry has grown at an average annual rate of 7.5% from 2008 to 2022. The industry has grown more than four times since 2012, with revenues rising to $358 billion, 14 times faster than overall U.S. employment growth.
Small and medium-sized businesses using PEOs have seen employment grow 7% to 9% faster than those companies that do not use PEO services, and have 10% to 14% lower employee turnover rates. PEO clients are mainly in three industries, which include professional, scientific, and technical services (22%), the manufacturing industry (13%), and the construction industry (12%). This data shows that these industries make up a large share of businesses using PEO services.
PEOs currently provide services to an estimated 208,000 businesses in the United States. This growth shows the industry’s ability to offer comprehensive HR solutions, which allow businesses to focus on core functions while ensuring compliance and accurate management of human resources.
What are the demographics and distribution of PEO client companies?
The demographics and distribution of PEO client companies show that nearly two-thirds are small to medium-sized businesses with 10 to 49 employees. Approximately 37% have 20 to 49 employees, while about 28% have 10 to 19 employees.
Industries with the highest PEO adoption include professional services at 22%, manufacturing at 13%, and construction at 12%. These three industries together account for nearly half of all PEO clients. Real estate and rental or leasing also show participation at 6%. Healthcare shows 11% of PEO clients, while retail trade shows lower adoption at 6%.
A large number of PEO clients are based in Florida, Texas, and California. Florida has about 25% of all PEO clients in the U.S., while Texas has 13% and California has 11%, together contributing another 25% to the overall PEO clients.
How do PEOs help companies with employment?
PEOs help companies with employment by providing HR services to about 208,000 businesses through the co-employment agreement, and employing approximately 4.5 million people across the United States. The number of employees supported by PEOs is about the same as the combined workforce of the four largest private employers in the U.S. For example, Walmart has around 2.1 million employees, Amazon has about 1.5 million, and companies like FedEx and UPS add 0.55 million and 0.49 million employees to the total number of employees.
PEOs help businesses create stable and competitive jobs as they give small businesses access to affordable HR services, such as Fortune 500-level benefits, compliance with labor laws, like FLSA (Fair Labor Standards Act), and risk management. 52% of PEO users have access to retirement plans for 10 to 49 employees, than 23% in companies that do not use a PEO.
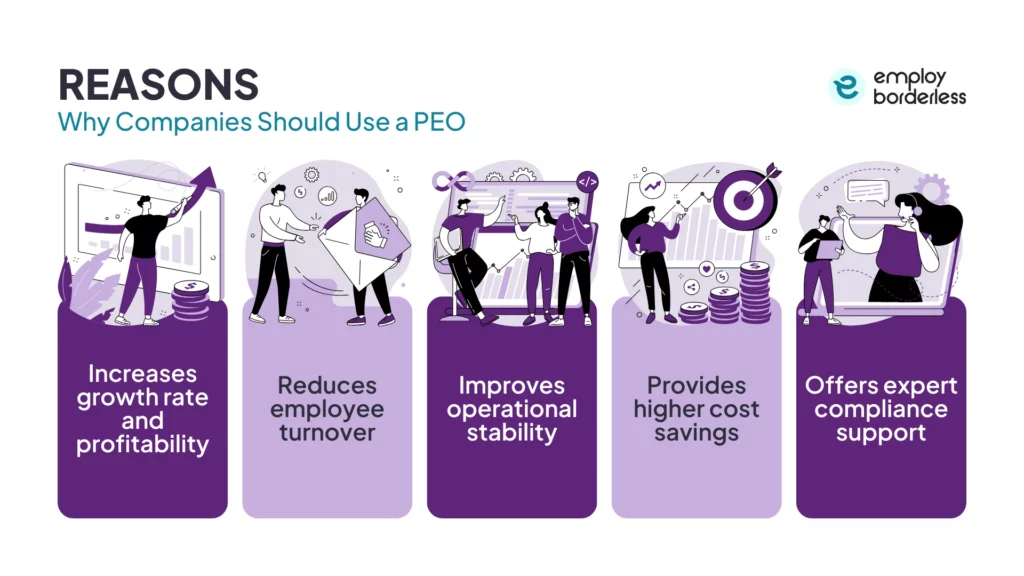
Why should companies use a PEO?
Companies should use a PEO as it increases growth rate and profitability, reduces employee turnover, improves operational stability, provides higher cost savings, and offers expert compliance support.
The reasons that businesses should use a PEO are listed below.
- Increases growth rate and profitability: Businesses that use PEOs experience growth two times faster than those companies that do not use a PEO. This third-party service provider also increases profitability by lowering HR-related costs and managing administrative tasks to increase employee productivity. They help businesses save costs on benefits, payroll processing, and compliance by using their economies of scale and expertise. This allows companies to focus more on income-producing activities, which leads to better financial performance overall.
- Reduces employee turnover: Reducing employee turnover means PEOs provide access to premium benefits to client businesses, such as health insurance, disability insurance, and retirement plans, which makes the company an attractive place for top talent. This access keeps employees loyal and dedicated to the employer and increases employee satisfaction and retention.
- Improves operational stability: Improving operational stability means PEOs simplify HR and administrative tasks by automating payroll processing, benefits enrollment, and compliance monitoring. PEOs offer HR technology that helps businesses reduce legal risks and lower operational disruptions, while also providing the stability required for long-term success.
- Provides higher cost savings: Providing higher cost savings means companies that use a PEO achieve an ROI of about 27.2%, so using PEOs is a cost-effective way to scale while accessing big-company benefits. Businesses also save about $1,775 per employee each year on average by using a PEO, while the average cost of a PEO is $1,395 per employee, which results in net savings overall.
- Offers expert compliance support: PEOs provide compliance support by making sure businesses comply with complex federal, state, and local employment laws, such as FMLA (Family and Medical Leave Act) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration). They ensure proper employee classification, accurate payroll tax management, benefits administration, and required safety and legal documentation, which reduces legal risks or lawsuits.
What to consider when choosing the PEO?
The factors to consider when choosing the PEO include determining your business needs, verifying the PEO’s certification, evaluating pricing and contract transparency, and reviewing its technology and integration.
Determine your business needs, such as payroll processing, compliance management, benefits administration, or multi-state expansion, when choosing a PEO. This helps you choose a PEO that matches your business goals and meets your compliance needs.
Verify the PEO’s certification, such as IRS certification, CPEO (Certified PEO), which confirms financial protection for clients and helps maintain tax compliance, or ESAC accreditation, which helps assess the PEO’s financial stability, ethical business conduct, and operational reliability.
Evaluate the pricing of the PEO, which is either a percentage of payroll or a PEPM fee (Per Employee Per Month) when choosing this outsourced HR model. This fee includes onboarding, benefits markups, or early termination charges, so it is important to carefully check the PEO contract for transparency and clear pricing to avoid unexpected expenses.
Review the HRIS platform of the PEO for features like employee self-service, mobile access, and scalable modules. Make sure it integrates with your existing systems when choosing a PEO, like accounting or ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), and if it offers APIs (Application Programming Interface) for smooth data migration.
How quickly do companies grow with a PEO?
Companies that use a PEO usually grow 7% to 9% more quickly per year than those businesses that do not use this third-party service. PEO clients grow twice as fast as compared to non-PEO businesses.
What is the ROI for companies using a PEO?
The ROI for companies using a PEO is about 27.2%, and this PEO ROI makes them a cost-effective solution for businesses. The PEO provides measurable savings to businesses while also supporting growth, compliance, and access to better employee benefits.
What is the average size of a PEO client company?
The average size of a PEO client company includes about 20 employees, with most clients ranging between 15 and 30. PEOs mainly serve small businesses but also support medium-sized and larger firms, which makes them suitable partners across different company sizes.
How big is the PEO industry?
The PEO industry is projected to generate $196.7 billion in U.S. revenue in 2025, with about 5,500 businesses. The PEO industry was valued at $66.23 billion globally in 2024 and is expected to grow to $73.58 billion in 2025. The global market is also expected to reach $170.8 billion by 2033 with an 11.1% CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate).
How much does a PEO cost per month for companies?
A PEO costs $100 to $200 per employee per month for companies, or a percentage of payroll, which is about 2% to 12%. The PEO cost simplifies expected operational expenses, ideal for stable teams, while the percentage-based model suits businesses with different hours, commissions, or seasonal staff.
How many types of PEOs do companies use?
There are five types of PEOs that companies use, which include ASO (Administrative Services Organization), full-service PEO, industry-specific PEO, CPEO (Certified PEO), and PEO alliances. These PEO types offer different levels of co-employment, specialization, and credibility.

Robbin Schuchmann is the co-founder of Employ Borderless, an independent advisory platform for global employment. With years of experience analyzing EOR, PEO, and global payroll providers, he helps companies make informed decisions about international hiring.
Ready to hire globally?
Get a free, personalized recommendation for the best EOR provider based on your needs.
Get free recommendations